PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
EINECS NO.
2930.90.9940
SMILES
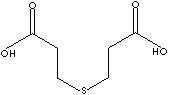
C(CCSCCC(O)=O)(O)=O
CLASSIFICATION
Antioxidant, Stabilizer
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
white crystalline powder
AUTOIGNITION
REFRACTIVE INDEX
GENERAL DESCRIPTION & EXTERNAL LINKS
Thioether is the sulfur analog of the ether (R-O-R), which sulfur atom replaces the oxygen. Sulfur and oxygen belong to the same group in the periodic table share similar chemical properties. The functional groups of sulfur and oxygen share similar chemical bonds and properties. Ethers can only be oxidized to peroxides (R-O-O-R). But thioethers (R-S-R) can be oxidized either to disulfides (R-S-S-R) or to sulfoxides (R-S(=O)-R) which can be further oxidized to the corresponding sulfones (R-S(=O)2-R) depending on the structure of the thioether.
Dimethyl Sulfide is the simplest thioether. The compound is a clear, flammable liquid; insoluble in water; boiling point 37C; with a distinctive garlic-like odor. It is used as a flavor component to enhance corn-related flavors. It is used as a presulfiding agent in the refinery and petrochemical production. The catalysts in hydrocracking, hydrodenitrification, hydrodesulfurization and reforming processes are used in oxide forms, which must be converted to the active sulfide form during the start-up to prevent the reduction of the catalysts to their base material by heat. The sulfur sources include alkyl mercaptans (methyl mercaptan, ethyl mercaptan, butyl mercaptan), dimethyl sulfide, dimethyl sulfoxide, dimethyl disulfide, and tert-nolyl polysulfide. They are used to modify the reactivity of catalysts to use in high temperature process furnaces. Dimethyl Sulfide is used to prevent the coke deposits which acts as a thermal insulator in the tube as it accumulates in pyrolysis furnaces. It is also used in steel mill furnaces to control dusting. Dimethyl Sulfide is included as a component of dangerous gases to detect the leaks by smell.
Thioethers have applications in organic synthesis as solvents as well as reagents. Acyclic thioethers with oxidized branches such as alcohol, aldehyde, ester, acid, beta-ketone, phenol demonstrate centres of greater polarity and additional functional sites for the additional uses. Cyclic sulfides containing oxidized carbon atoms would involve extensive S-oxidation. Thioethers are involved in versatile in the synthesis of specific compound classes include agricultural chemical, property-enhancing additives, pharmacological drugs, chemical resistant polymers, detergents, and rubber antioxidants.
3,3'-Thiodiproprionic acid is used as a primary or secondary antioxidant and color stabilizer for polymers including polyolefins, styrenics, rubbers and soap industry. It is also used as an intermediate for the synthesis of organic compounds.
http://www.sciencedirect.com/
Mechanisms of antioxidant action: the nature of the
redox behaviour of thiodipropionate esters in polypropylene
http://www.epa.gov/
....DLTDP,
DTTDP and DSTDP are all produced by reacting the same intermediate,
thiodipropionitrile (TDPN), with different fatty alcohols. DLTDP
uses lauryl alcohol, DTTDP uses iso-tridecyl alcohol and DSTDP uses
stearyl alcohol. The reaction of TDPN with the alcohols is an esterification
using acid catalysts (hydrochloric acid and sulfuric acid). Water
is removed under vacuum to drive the esterification to completion.
Then the catalyst is neutralized and salts and impurities removed
in a series of filtrations and washes. The molten DLTDP and DSTDP
are converted to solid products by flaking and packaged. The liquid
DTTDP product is drummed. The TDPN intermediate is made by reacting
acrylonitrile and sodium sulfhydrate in aqueous solution. The resulting
aqueous phase is split off, the product phase washed with water
and the remaining TDPN used to make the thioesters. The reactions
all take place in enclosed reactors, thus limiting potential worker
exposure. The DLTDP, DTTDP and DSTDP all have very low vapor pressures
at ambient temperatures so the risk of vapor contact during manufacture
and drumming is relatively low. These chemicals are used by our
customers who add them to variety of plastics such as polyethylene,
polyolefins (mostly polypropylene), and polystyrene. Common use
levels of DLTDP and DSTDP are 0.1 to 0.2 %. The polymers are then
further processed into items such as washing machine agitators,
battery cases, food packaging materials, and household appliances.
.....
APPEARANCE
white crystalline powder
98.0% min
OTHER INFORMATION
|
Thiodipropionates |
|
|
Product |
CAS RN. |
|
Dilauryl thiodipropionate |
123-28-4 |
| Diethyl 3,3'-thiodipropionate | 673-79-0 |
| Distearyl thiodipropionate | 693-36-7 |
| Diethyl 3,3'-dithiodipropionate | 1609-40-1 |
| Dicetyl thiodipropionate | 3287-12-5 |
| Dioctyltin-3,3'-thiodipropionate | 3594-15-8 |
| Dimethyl 3,3'-thiodipropionate | 4131-74-2 |
| Dibutyltin 3,3'-thiodipropionate | 4981-24-2 |
| Distearyl 3,3'-dithiopropionate | 6729-96-0 |
| Dibutyl 3,3'-thiodipropionate | 6975-31-1 |
| Bis(2-ethylhexyl) 3,3'-thiodipropionate | 10526-15-5 |
| Di(tridecyl) thiodipropionate | 10595-72-9 |
| Lauryl stearyl 3,3'-thiodipropionate | 13103-52-1 |
| Dimethyl 3,3'-dithiodipropionate | 15441-06-2 |
| Dimyristyl thiodipropionate | 16545-54-3 |
| Dioleyl 3,3'-thiodipropionate | 17043-10-6 |
| Dimethyl 3,3'-trithiodipropionate | 20707-94-2 |
| Diisobutyl 3,3'-thiodipropionate | 22695-02-9 |
| Didodecyl thiodipropionate | 31852-09-2 |
| Dioctadecyl thiodipropionate | 31852-10-5 |
| Diisooctyl 3,3'-dithiodipropionate | 33881-78-6 |
| Bis(2-mercaptoethyl) 3,3'-thiodipropionate | 67874-44-6 |
| Bis(2,3-dihydroxypropyl) 3,3'-dithiodipropionate | 68928-35-8 |
| Bis(2,3-dihydroxypropyl) 3,3'-thiodipropionate | 68928-36-9 |